System Development: 7 Ultimate Power Strategies for Success
System development is the backbone of modern technology, shaping how businesses operate and innovate. From simple apps to complex enterprise solutions, mastering this process unlocks efficiency, scalability, and competitive advantage in today’s digital world.
What Is System Development and Why It Matters

System development refers to the structured process of designing, building, testing, and deploying information systems that meet specific organizational needs. It’s not just about writing code—it’s about solving real-world problems through technology. Whether it’s automating workflows, improving data management, or enhancing customer experiences, system development drives digital transformation across industries.
Defining System Development in Modern Context
In today’s tech-driven landscape, system development encompasses everything from mobile applications and cloud platforms to AI-powered analytics tools. It involves a lifecycle approach where each phase contributes to the creation of a robust, secure, and scalable solution. According to the IEEE Computer Society, effective system development integrates technical expertise with business strategy to deliver measurable value.
- It bridges the gap between business requirements and technological implementation.
- It supports innovation by enabling rapid prototyping and iteration.
- It ensures alignment with regulatory, security, and performance standards.
“System development is not just a technical task—it’s a strategic enabler for organizational growth.” — MIT Technology Review
Core Objectives of System Development
The primary goal of system development is to create systems that are functional, reliable, and maintainable. However, deeper objectives include reducing operational costs, increasing agility, and supporting long-term scalability. A well-executed system development project can transform outdated processes into streamlined, automated workflows.
- Improve operational efficiency through automation.
- Enhance decision-making with real-time data access.
- Support integration with existing IT infrastructure.
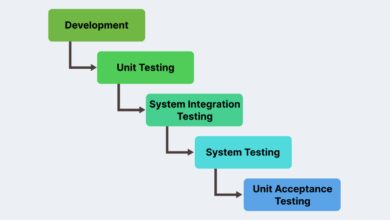
The System Development Life Cycle (SDLC) Explained
The System Development Life Cycle (SDLC) is a foundational framework used to plan, design, develop, test, deploy, and maintain software systems. It provides a clear roadmap for managing projects efficiently and minimizing risks. SDLC is widely adopted because it promotes discipline, accountability, and quality assurance throughout the development process.
Phases of the SDLC
SDLC consists of several distinct phases, each critical to the success of the final product. These phases ensure that all stakeholders—from developers to end-users—are aligned and that the system meets its intended goals.
- Planning: Identifying project scope, resources, timelines, and feasibility.
- Analysis: Gathering and documenting user requirements in detail.
- Design: Creating system architecture, data models, and interface layouts.
- Implementation: Writing code and building the actual system components.
- Testing: Validating functionality, performance, and security.
- Deployment: Releasing the system into production environments.
- Maintenance: Providing updates, patches, and enhancements post-launch.
Each phase feeds into the next, forming a cohesive workflow. For more insights on SDLC best practices, visit the official SDLC methodology guide.
Benefits of Following SDLC
Adopting SDLC brings numerous advantages, especially for large-scale or mission-critical system development projects. It reduces ambiguity, improves collaboration, and enhances transparency across teams.
- Reduces project failure rates by up to 40% (based on PMI reports).
- Enables better risk management through early detection of issues.
- Facilitates stakeholder involvement at every stage.
- Improves documentation and future maintainability.
“Without a structured lifecycle, even the most talented developers can deliver chaotic results.” — Harvard Business Review
Popular System Development Methodologies
There are multiple approaches to system development, each suited to different project types, team sizes, and business environments. Choosing the right methodology can significantly impact project speed, flexibility, and outcome quality.
Waterfall Model: The Traditional Approach
The Waterfall model is one of the earliest and most linear system development methodologies. It follows a strict sequence where each phase must be completed before moving to the next. This approach works well for projects with clearly defined requirements and minimal expected changes.
- Ideal for government, healthcare, or regulated industries.
- Offers strong documentation and traceability.
- Limited flexibility makes it less suitable for dynamic environments.
Despite criticism for rigidity, the Waterfall model remains relevant in sectors where compliance and audit trails are paramount. Learn more at British Computer Society.
Agile: The Modern Standard for Flexibility
Agile has become the go-to methodology for most contemporary system development initiatives. It emphasizes iterative development, continuous feedback, and cross-functional teamwork. Instead of delivering one final product, Agile delivers working increments in short cycles called sprints.
- Encourages customer collaboration and adaptive planning.
- Allows for rapid response to changing requirements.
- Improves product quality through frequent testing and reviews.
According to the Agile Alliance, over 70% of software teams now use Agile or hybrid models. Frameworks like Scrum and Kanban fall under this umbrella, offering structured yet flexible paths for system development.
DevOps: Bridging Development and Operations
DevOps extends Agile principles by integrating development (Dev) and IT operations (Ops) into a seamless pipeline. It focuses on automation, continuous integration (CI), and continuous delivery (CD) to accelerate system development and deployment.
- Reduces time-to-market for new features and fixes.
- Enhances system reliability through automated testing and monitoring.
- Promotes a culture of shared responsibility and collaboration.
Companies like Amazon and Netflix rely heavily on DevOps to maintain high availability and rapid innovation. For best practices, check out DevOps.com.
Key Roles in System Development Teams
A successful system development project requires a diverse team with complementary skills. Each role plays a crucial part in translating ideas into functional, user-friendly systems.
Business Analysts: The Requirement Translators
Business analysts act as intermediaries between stakeholders and technical teams. They gather, analyze, and document business needs, ensuring that the final system aligns with organizational goals.
- Conduct interviews, workshops, and surveys to capture requirements.
- Create use cases, process flows, and requirement specifications.
- Validate that developed features meet original business objectives.
“A great business analyst turns vague ideas into actionable blueprints.” — Forbes Technology Council
Software Developers and Engineers
Developers are the builders of the system. They write code, implement algorithms, and integrate components based on design specifications. Depending on the project, they may specialize in front-end, back-end, full-stack, or mobile development.
- Use programming languages like Python, Java, JavaScript, or C#.
- Follow coding standards and version control practices (e.g., Git).
- Collaborate with QA teams to fix bugs and optimize performance.
Modern developers also engage in code reviews and pair programming to ensure quality and knowledge sharing.
Quality Assurance (QA) and Testers
QA professionals ensure that the system functions correctly and meets quality standards. They design test cases, execute manual and automated tests, and report defects.
- Perform functional, regression, performance, and security testing.
- Use tools like Selenium, JUnit, or Postman for automation.
- Work closely with developers to resolve issues before deployment.
Effective QA reduces post-release failures and enhances user trust in the system.
Tools and Technologies in System Development
The right tools can dramatically improve productivity, collaboration, and code quality in system development. From integrated development environments (IDEs) to cloud platforms, technology stacks shape how systems are built and maintained.
Integrated Development Environments (IDEs)
IDEs provide a comprehensive workspace for coding, debugging, and testing. They combine text editors, compilers, and debuggers into a single application, streamlining the development process.
- Popular IDEs include Visual Studio Code, IntelliJ IDEA, and Eclipse.
- Support syntax highlighting, auto-completion, and plugin ecosystems.
- Enable real-time collaboration through features like Live Share.
For developers, choosing the right IDE can save hundreds of hours over a project’s lifecycle.
Version Control Systems
Version control is essential for tracking changes, managing codebases, and enabling team collaboration. It allows multiple developers to work on the same project without conflicts.
- Git is the most widely used version control system.
- Platforms like GitHub, GitLab, and Bitbucket host repositories and offer CI/CD integration.
- Support branching, merging, and pull requests for code review.
According to GitHub’s Octoverse Report, over 100 million developers use Git worldwide, making it a cornerstone of modern system development.
Cloud Platforms and DevOps Tools
Cloud computing has revolutionized system development by providing scalable infrastructure, on-demand resources, and global deployment capabilities.
- Major providers include AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform.
- Offer services like virtual machines, databases, serverless functions, and AI APIs.
- Integrate with DevOps pipelines for automated builds and deployments.
These platforms reduce upfront costs and allow startups and enterprises alike to innovate faster. Explore AWS’s developer resources at AWS Developer Center.
Challenges in System Development and How to Overcome Them
Despite advancements in tools and methodologies, system development remains fraught with challenges. Recognizing these obstacles early and implementing mitigation strategies is key to project success.
Scope Creep and Requirement Volatility
One of the most common issues in system development is scope creep—the uncontrolled expansion of project requirements. This often leads to delays, budget overruns, and team burnout.
- Solution: Implement change control processes and prioritize features using MoSCoW (Must-have, Should-have, Could-have, Won’t-have).
- Use Agile sprints to deliver value incrementally while managing evolving needs.
- Engage stakeholders regularly to align expectations.
“The biggest risk in system development isn’t technology—it’s unclear or shifting requirements.” — Project Management Institute
Technical Debt Accumulation
Technical debt refers to the long-term consequences of taking shortcuts during development—such as writing quick-and-dirty code or skipping tests. While it may speed up initial delivery, it hampers future scalability and maintenance.
- Solution: Allocate time for refactoring and code cleanup in every sprint.
- Enforce code quality standards using linters and static analysis tools.
- Track technical debt in issue trackers and address it proactively.
Organizations like Spotify use technical debt dashboards to monitor and manage this invisible burden.
Security and Compliance Risks
With rising cyber threats, security can no longer be an afterthought in system development. Vulnerabilities introduced during coding or configuration can lead to data breaches and legal liabilities.
- Solution: Adopt Secure Software Development Lifecycle (SSDLC) practices.
- Integrate security testing (SAST, DAST) into CI/CD pipelines.
- Ensure compliance with regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI-DSS.
The OWASP Top 10 provides a critical checklist for identifying common security risks in web applications.
Future Trends Shaping System Development
The field of system development is evolving rapidly, driven by advances in artificial intelligence, low-code platforms, and decentralized architectures. Staying ahead of these trends is crucial for organizations aiming to remain competitive.
AI and Machine Learning Integration
Artificial intelligence is transforming system development by enabling smarter applications that learn from data and adapt over time. AI-powered tools are also assisting developers in writing code, detecting bugs, and optimizing performance.
- GitHub Copilot uses AI to suggest code snippets in real time.
- ML models are embedded into systems for predictive analytics and personalization.
- Natural language processing (NLP) allows users to interact with systems via voice or chat.
As AI becomes more accessible, system development will shift from manual coding to guided automation.
Low-Code and No-Code Platforms
Low-code and no-code platforms empower non-developers (citizen developers) to build applications using visual interfaces and drag-and-drop tools. This democratization of system development accelerates innovation across departments.
- Platforms like Microsoft Power Apps, OutSystems, and Bubble are gaining traction.
- Reduce dependency on IT teams for small-to-medium business apps.
- Allow faster prototyping and experimentation.
However, governance and scalability remain concerns when adopting these platforms enterprise-wide.
Blockchain and Decentralized Systems
Blockchain technology introduces new paradigms for system development, particularly in areas requiring transparency, immutability, and trustless interactions.
- Used in supply chain tracking, digital identity, and smart contracts.
- Requires specialized knowledge in cryptography and distributed consensus.
- Integrates with traditional systems via APIs and middleware.
While still emerging, blockchain-based system development is expected to grow significantly in finance, healthcare, and public services.
Best Practices for Successful System Development Projects
Following proven best practices can dramatically increase the likelihood of delivering a high-quality system on time and within budget. These practices span planning, execution, and post-deployment phases.
Start with Clear Requirements and Stakeholder Alignment
One of the top reasons for project failure is poorly defined or misunderstood requirements. Invest time upfront in gathering detailed, validated requirements from all stakeholders.
- Use techniques like user stories, personas, and journey mapping.
- Validate assumptions through prototypes or mockups.
- Document requirements in a centralized repository accessible to all team members.
Clear requirements serve as the foundation for every subsequent phase of system development.
Adopt Iterative Development and Continuous Feedback
Rather than waiting until the end to show results, adopt an iterative approach where working versions are delivered frequently. This allows for early feedback and course correction.
- Break projects into manageable sprints or milestones.
- Conduct regular demos with stakeholders to validate progress.
- Incorporate feedback loops into your development cycle.
“The shortest path to a great system is through constant iteration and user validation.” — Lean Startup Methodology
Prioritize Testing, Documentation, and Scalability
Too often, testing and documentation are treated as afterthoughts. In reality, they are critical for long-term success and system maintainability.
- Implement automated testing at unit, integration, and end-to-end levels.
- Maintain up-to-date technical and user documentation.
- Design systems with scalability in mind—anticipate future growth in users and data.
Well-documented, thoroughly tested systems are easier to support, upgrade, and extend.
What is system development?
System development is the process of creating, implementing, and maintaining software systems to meet specific business or user needs. It involves stages like planning, analysis, design, coding, testing, deployment, and maintenance, often guided by frameworks like SDLC.
What are the main phases of system development?
The main phases include planning, requirement analysis, system design, implementation (coding), testing, deployment, and maintenance. These phases form the System Development Life Cycle (SDLC), which ensures structured and efficient project execution.
Which methodology is best for system development?
The best methodology depends on the project. Agile is ideal for dynamic environments requiring flexibility, Waterfall suits projects with fixed requirements, and DevOps excels in continuous delivery scenarios. Many organizations use hybrid models tailored to their needs.
How do you manage risks in system development?
Risks are managed through thorough planning, stakeholder communication, iterative development, code reviews, automated testing, and security audits. Using frameworks like SSDLC and maintaining technical debt logs also help mitigate potential issues.
What tools are essential for modern system development?
Essential tools include IDEs (e.g., VS Code), version control systems (e.g., Git), cloud platforms (e.g., AWS), CI/CD pipelines (e.g., Jenkins), and collaboration tools (e.g., Jira). These tools enhance productivity, collaboration, and deployment efficiency.
System development is a dynamic and essential discipline that powers innovation across industries. By understanding its lifecycle, embracing modern methodologies like Agile and DevOps, leveraging powerful tools, and anticipating future trends like AI and low-code platforms, organizations can build systems that are not only functional but also resilient and scalable. Success lies in balancing technical excellence with strategic vision, clear communication, and continuous improvement. Whether you’re building a simple app or a complex enterprise solution, mastering system development is the key to thriving in the digital age.
Further Reading: